

The NGSP’s goal is to standardize A1C results to those of the DCCT trial, a process termed traceability. 7,8 In the 1990s, the National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program (NGSP) was developed to formalize A1C testing.
9. hemoglobin a1c normal range trial#
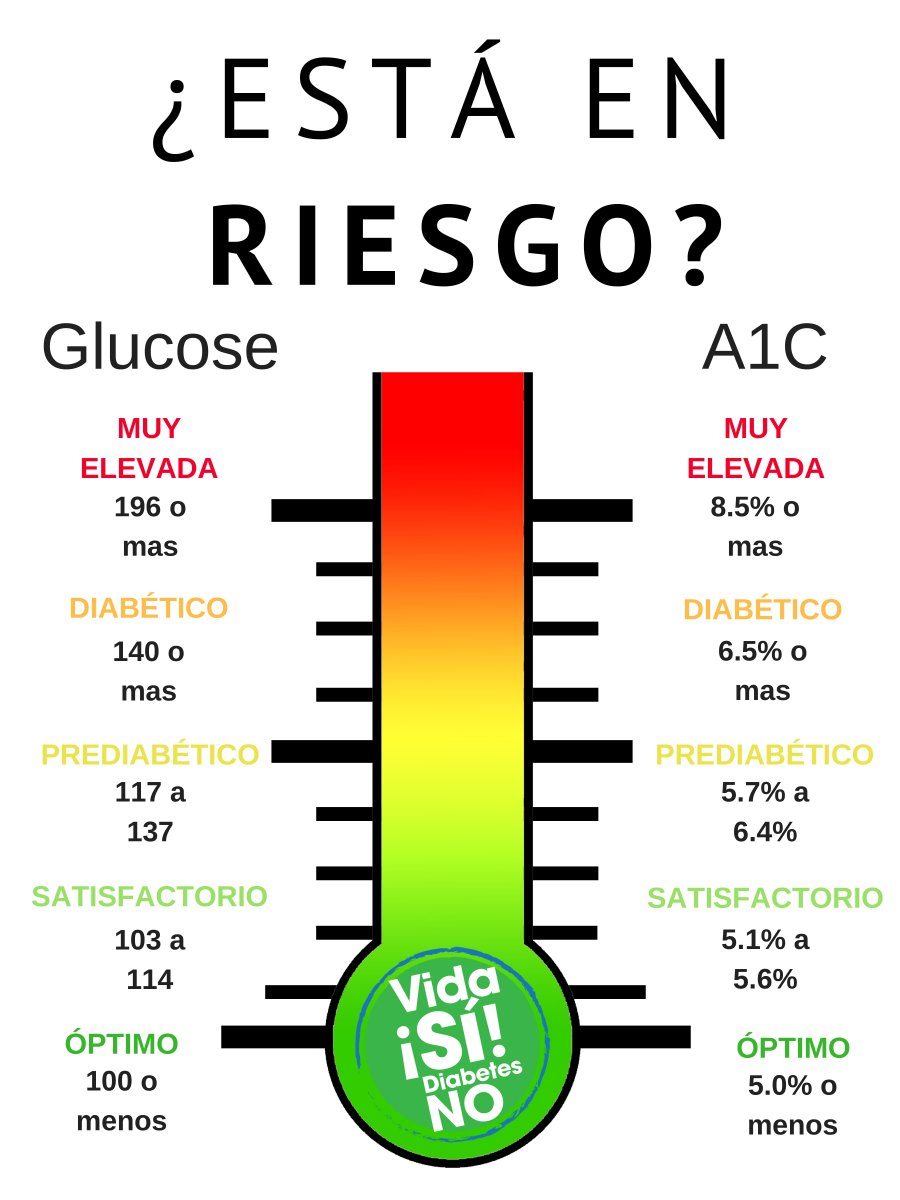
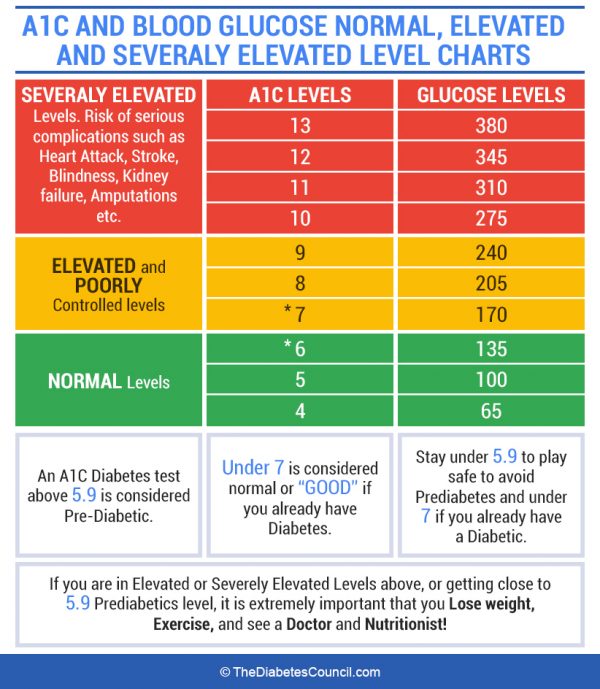
This shift in policy happened following the publication of the results of the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) and The United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS), which found that reductions in A1C resulted in decreased risk of microvascular complications in type 1 DM (T1DM) and type 2 DM (T2DM) patients, respectively. 4 It was later incorporated into American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines and was subsequently adopted by the World Health Organization. 2Ī1C testing gained acceptance as a diagnostic tool for diabetes mellitus (DM) in 2009, when it was formally endorsed by an International Expert Committee that was examining its role. 1-3 A1C represents a weighted average, with approximately 50% of the value due to the mean blood glucose (BG) concentrations in the 30 days prior to sampling BG concentrations from the previous 90 to 120 days make up about 10% of the final total A1C value. Therefore, A1C is used to measure glycemic control over the previous 3 months. This process is dependent on ambient glucose concentrations and occurs throughout the 120-day lifespan of the red blood cell (RBC). Patient-specific and assay-specific interferences that exist can potentially result in inaccuracies in A1C readings.A1C results from the nonenzymatic glycation of the amino (N)-terminal valine residue of hemoglobin A.
Limitations have been identified surrounding the use of A1C as a diagnostic aid in certain patient populations. One of the guidelines, the American College of Physicians’ guidance statement, has generated controversy because it has recommended higher target glycemic goals than the other recommendations. Three of the latest clinical guidelines on DM address diagnosis and management. ABSTRACT: Since 2010, A1C, the glycosylated form of hemoglobin, has been recognized by diabetes mellitus (DM) clinical guidelines as a diagnostic tool.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
